(d) none of these
Case Study B - Parasites
Several plants do not have chlorophyll (green pigment) and cannot perform photosynthesis. They obtain nutrition from a host plant and are called parasites. A parasite gives no benefit to its host. Instead, some parasites cause extreme damage to their hosts.
Witchweed or Striga is one such parasite. It is a small plant with pretty flowers. It needs a host plant in order to germinate and grow into a young plant. Once it grows, it can create its own food. However, as a sapling, it attaches itself to the roots of its host plant and uses all its nutrition. In the process, the host plant either cannot grow fully or dies completely. Striga especially affects farmers in Asia, Africa, America and Australia as they attach themselves to crops like sugarcane, rice and corn. They can reduce the yield or destroy the entire crop.
Question 1:

i. Which of the plants shown in Fig 1.6 are parasites?
Answer:. (i) Bird’s Nest Orchid
ii. What factors about the plant did you consider while answering Part i.?
a. Colour b. Shape c. Type d. Size
Answer a. Colour
Question2 :
A group of scientists in Kenya are trying to help farmers whose crops are affected by Striga/witchweed. They have found 3 chemical solutions that prevent Striga seeds from germinating in the roots of the host plant. They are called Nij1, GR24 and MP1.
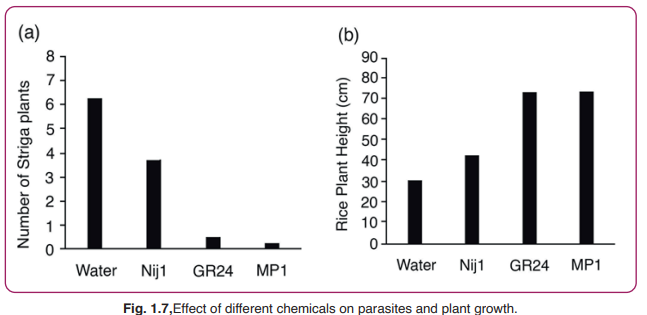
To test the effect of the solutions, they apply the solutions to a collection of four groups of Striga infested rice plant pots. They observe the plants to see whether they are effective in controlling the growth of the parasite or not. Here are their results:
Answer the following questions based on the above results:
I. Look at Graph (a). Apart from the three solutions Nij1, GR24 and MP1, why did the experimenters also look at the impact of just water?
Answer: The experimenters have included water to see how many Strigas would grow in a pot if
no other solution is applied to the rice plant. That way the scientists can infer if adding
the other chemical solutions has any impact on the germination of Striga plants
ii. As a farmer, which solution should I use to prevent Striga growth?
a. Water b. Nij1 c. GR24 d. MP1
Answer d. MP1
Explanation: MP1 is most effective in controlling the growth of the parasitic plants and it
also enables the rice plant to reach its optimal height.
iii.Which of the following shows that Striga has a negative effect on the growth of its host - the rice plant?
a. Graph (a) b. Graph (b)
c. Both Graph (a) and Graph (b) d. No such conclusion can be drawn from either of
the two graphs.
Answer bGraph (b)
Case Study C - Photosynthesis - CO2
In this activity, one leaf is exposed to potassium hydroxide, which will absorb carbon dioxide from the surrounding air. It is then exposed to light and tested for starch (carbohydrate). The experiment is designed to test whether carbon dioxide is needed for the plant to produce starch/carbohydrates.




Question 1 Adil was surprised to see that the plant grew by a few cm even when it was kept in the dark. He concluded that photosynthesis was possible even in the absence of light. Rehana countered his conclusion by giving the following statements:
Assertion(A): In the dark, plants use up the food stored in the form of starch to grow.
Reason(R): Food cannot be prepared in the absence of sunlight.
What is your opinion about this debate between the two?
a. Adil is right.
B. Adil is wrong and Rehana gave the correct explanation for the observed growth.
c. Both Adil and Rehana made incorrect conclusions.
D. Adil is right and Rehana's assertion is incorrect though her reason is right.
b. Adil is wrong and Rehana gave the correct explanation for the observed growth.
Question 2 Rehana performed the experiment described in Case Study C herself. After making the leaves colourless, when she put iodine, she observed that none of the leaves turned blue-black. What can be the possible source of error?
The leaves were not de-starched properly initially, when the plant was placed in the dark room.
The leaf chosen as Control could not receive proper sunlight.
The leaves were not boiled in water for a sufficient period of time to kill the cells.
There was a hole in the Test bag through which CO2 (carbon dioxide) could enter
Question 3 The experiment described in Case Study C was repeated two more times, without any error. In one of the repetitions, the plant was kept in the dark room for 24 hours and in the other one, the plant was kept in the dark room for 120 hours. The same process was followed afterwards to test if CO2 (carbon dioxide) is required to produce starch. The test results are shown in Table 1.1.
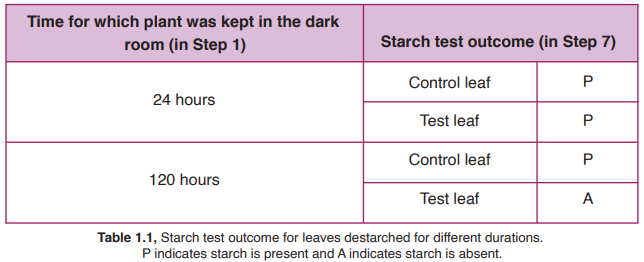
What accounts for the starch detected in the Test leaf of the plant that was kept in the dark room for 24 hours?
Starch was already present in the Test leaf before the leaf was enclosed in the potassium hydroxide bag.
Starch was prepared by the Test leaf in Step 2 in the absence of CO2 2. (carbon dioxide).
1 only b. 2 only
c. Both 1 and 2 d. An error made in the later stages of the activity.
Question 4. CO2 concentration in air is indicated in terms of parts per million or ppm. 100 ppm would mean that 100 particles of CO2 are present in 1,000,000 air particles. The graph in Fig. 1.8 shows the effect of CO2 levels on the plant growth rate.
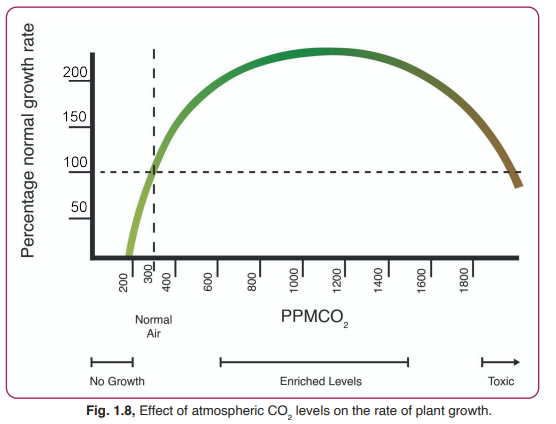
I. On the basis of the activity given in Case Study C and Fig. 1.8, which of the following inferences are correct? Select all that apply.
CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.
Plant growth increases with increase in atmospheric CO2 , only up to a certain level
A continuous increase in atmospheric CO2 after a certain level can have a negative effect on plant growth. \
CO2 is not necessary for photosynthesis but it enhances plant growth.
Answer a. CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.b. Plants growth increases with increase in atmospheric CO2, only up to a certain level.c. A continuous increase in atmospheric CO2after a certain level can have a negativeeffect on plant growth.
Ii. Over the past 60 years, CO2 in the Earth’s atmosphere has increased by nearly 100 ppm. It stands at 420 ppm at present. How do you think it might have affected plant life on the planet?
Answer: The rate of photosynthesis has increased for plants on Earth
1. Photosynthesis is an important process for life on earth because
(a) it is the primary source of all food on earth
(b) it is responsible for the release of oxygen
(c) it is the only natural process responsible for the utilisation of sunlight
(d) All of the above
2. The main purpose of photosynthesis is to
(a) consume CO2
(b) produce ATP
(c) convert light energy into Chemical energy
(d) produce starch
3. The process of digestion in our digestive system involves
(a) conversation of complex substances into simple form
(b) absorption of monomers by the body
(c) conversion of monomers into polymers
(d) absorption of water and food
4. Digestion in the digestive system of humans is accomplished by
(a) mechanical and Chemical processes
(b) chemical processes only
(c) mechanical processes only
(d) none of the above
5. A baby boy aged two years is admitted to play school and passed through a dental checkup . The dentist observed that the boy had twenty teeth. Which teeth were absent.
(a) Incisors
(b) Canines
(c) Premolars
(d) Molars
6. The primary dentition in human differs from permanent dentition not having one of the following type of teeth.
(a) Canine
(b) Premolars
(c) Molar
(d) incisor
7. Write the dental formula of human being.
Ans
8. How many deciduous teeth are present in humans?
(a) 22
(b) 24
(c) 20
(d) 18
9.The hard chewing surface of teeth is made up of :
(a) Dentine
(b) enamel
(c) teeth
(d) bone
10. During intake of food , the entry of food into the glottis (opening of windpipe) is prevented by
(a) Glottis itself
(b) air present in windpipe
(c) annular rings of pharynx
(d) epiglottis
11. Length of oesophagus is:
(a) 25 cm
(b) 55 cm
(c) 33 cm
(d) 45 cm
12. Salivary glands pour their secretion into
(a) Stomach
(b) blood
(c) buccal cavity
(d) intestine
13. Which is the largest gland of human body?
(a) Liver
(b) Gastric gland
(c) Pancreas
(d) intestine
14. Bile juice is stored in which organ of human body?
(a) Gall bladder
(b) Liver
(c) kidney
(d) Pancreas
15. Which food component gets 30% hydrolysed in mouth?
(a) Starch
(b) Protein
(c) Fats
(d) Nucleic acids
16. The secretion released into the small intestine are :
(a) bile and pancreatic juice
(b) succus entericus only
(c) pancreatic juice, bile and intestinal juice
(d) pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
17.